Technical notation and terms
Below is a summary of the notation conventions used in this book, followed by a table of technical terms. The table shows the different forms that each term can take, to help you select the appropriate one for your purposes.
Summary of notation conventions
X_Z
Represents the distribution frame of a linguistic unit. The blank represents the relevant unit. X and Z represent the linguistic units immediately before and after the relevant unit, e.g.
Det_N represents the distribution frame of Adj
Det represents the distribution frame of N
{ }
Curly brackets are used in morphology to enclose morphemes, e.g.
the word unhappiness comprises the morphemes {un-}, {happy}, and {-ness}
the word challenging comprises the morphemes {challenge} and {-ing}
Curly brackets (or braces) are also used in syntax, in phrase structure (PS) rules, to denote alternative constituents, e.g.
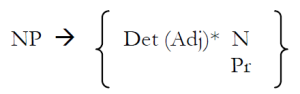
[ ]
Phonetic symbols appear within square brackets, e.g. [f], [b], [m] Phonetic transcriptions appear within square brackets.
Allophones appear within square brackets.
/ /
Phonemes appear within slashes, e.g. /f/, /b/, /m/ Phonemic representations appear within slashes.
→
Used in PS rules to mean ‘expands into’, ‘is constituted by’, ‘is rewritten as’
( )
Used in PS rules to denote optional constituents
*
An asterisk before an example indicates that the use of language in the example is ungrammatical (syntactically unacceptable or non-occurring)
An asterisk after a linguistic unit indicates one or more of that unit
#
before an example, indicates that the use of language in the example is semantically odd or unacceptable.
Technical terms and how to use them appropriately
|
Noun use |
Verb use |
Adjective use |
Adverb use |
Agent use |
|
active |
– |
active |
actively |
– |
|
adjective |
adjectivise |
adjectival |
adjectivally |
– |
|
adjunct |
adjoin |
adjunct |
– |
– |
|
adverb |
– |
adverbial |
adverbially |
– |
|
affix affixation |
affix |
affixed (word) |
– |
– |
|
agreement |
agree |
– |
– |
– |
|
ambiguity |
– |
ambiguous |
ambiguously |
– |
|
anaphora |
anaphorise |
anaphoric |
anaphorically |
– |
|
articulation |
articulate |
articulated |
– |
articulator |
|
compound |
compound |
compounded |
– |
– |
|
conjunction |
conjoin |
conjunctional |
conjunctionally |
– |
|
conversion |
convert |
converted |
– |
– |
|
coordination |
coordinate |
coordinate(d) |
coordinately |
coordinator |
|
derivation |
derive |
derived (word) derivational (affix) |
derivationally |
– |
|
diagram |
diagram |
diagrammatic |
diagrammatically |
– |
|
grammar |
grammaticise |
grammatical |
grammatically |
grammarian |
|
Noun use |
Verb use |
Adjective use |
Adverb use |
Agent use |
|
head |
head |
headed |
– |
– |
|
inflection |
inflect |
inflected (word) inflectional (affix) |
inflectionally |
– |
|
lexicon |
lexicalise |
lexical |
lexically |
lexicologist |
|
linguistics |
– |
linguistic |
linguistically |
linguist |
|
morphology |
– |
morphological |
morphologically |
morphologist |
|
noun |
nominalise |
nominal |
nominally |
– |
|
object |
– |
object |
– |
– |
|
passive |
passivise |
passive |
passively |
– |
|
phonetics |
– |
phonetic |
phonetically |
phonetician |
|
phonology phoneme |
– |
phonological phonemic |
phonologically phonemically |
phonologist |
|
phrase |
phrase |
phrasal |
– |
– |
|
plural |
pluralize |
plural |
– |
– |
|
preposition |
– |
prepositional |
prepositionally |
– |
|
pronoun |
pronominalise |
pronominal |
pronominally |
– |
|
science |
– |
scientific |
scientifically |
scientist |
|
semantics |
– |
semantic |
semantically |
semantician semanticist |
|
singular |
– |
singular |
– |
– |
|
subject |
– |
subject |
– |
– |
|
subordination |
subordinate |
subordinate(d) |
subordinately |
subordinator |
|
syntax |
– |
syntactic |
syntactically |
syntactician |
|
verb |
verbalise |
verbal |
verbally |
– |
Attribution
This chapter has been modified and adapted from The Language of Language. A Linguistics Course for Starters under a CC BY 4.0 license. All modifications are those of Régine Pellicer and are not reflective of the original authors.

